Optical fiber transmission has low loss, is suitable for long-distance transmission, and is resistant to electromagnetic interference, but the cost is high. In real applications, it is mainly electrical signals, and optical signals will eventually be converted into electrical signals through photoelectric converters. What are the key indicators of analogue signal acquisition in electrical signals?

1. Resolution: refers to the number of ADC bits, such as the difference between 12-bit ADC and 16-bit ADC. In the real world, the signal is continuous, and after ADC sampling, a series of discrete values are obtained. Within the same voltage range, the higher the ADC bits, the more voltage steps can be represented, and the voltage steps are 2 resolutions. The higher the number of ADC bits, the more accurately the real signal can be restored.
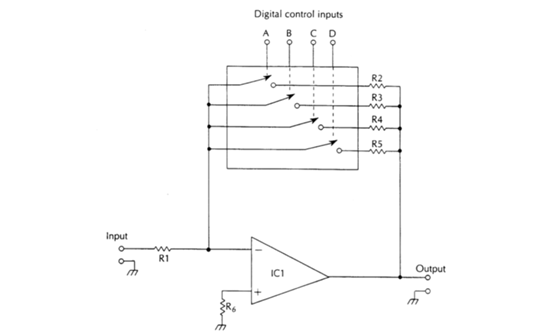
2. Range: refers to the signal range that can be measured by the data acquisition device. Advanced data acquisition equipment has a variable range, and the range can be set, which can be realized through an internal programmable gain amplifier.
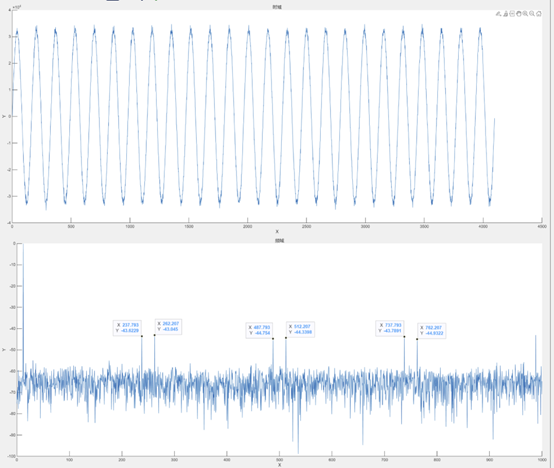
3. Sample Rate fs: refers to the number of information samples collected per second. The analogue signal is a continuous time-variable signal, and the sampling signal obtains a series of discrete sampling points at the sampling rate to be determined. Theoretically, the faster it is collected, the closer the information sampled is to the actual signal. For rapidly changing signals, they can be expressed in two dimensions: time domain and frequency domain.
4. Absolute Accuracy: In actual measurement, there is always a certain deviation between the measured value and the real input value. Although this degree of uncertainty is not fixed every time it is measured, it has a range, which is the maximum nominal error of the data acquisition device is absolute accuracy.

5. Calibration: Because the electronic components of the data acquisition equipment will drift naturally over time, the accuracy will be affected, so the calibration hardware should be calibrated regularly to ensure accuracy. Calibration includes two steps. The first is "verification", which verifies the accuracy of equipment data collection through the standard signal source. The second step is "correcting". There are two ways of "correcting", one is hard calibration and the other is soft calibration.

Post time: Mar-18-2025

